02 Apr Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Symptoms, Causes, and Effective Treatments
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is a common condition affecting many individuals, particularly those who engage in activities that require repetitive hand motions. Understanding this syndrome is crucial for anyone experiencing discomfort in their hands or wrists. In this article, we will delve into what Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is, explore its common symptoms, examine the causes and risk factors, discuss the diagnosis process, and review effective treatment options. Additionally, we will offer valuable tips for preventing this condition and maintaining overall hand health. Whether you’re a professional in a hands-on job or simply looking to understand your own wrist pain, our comprehensive guide will provide the insights you need.
Key Takeaways
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is a condition characterized by compression of the median nerve in the wrist.
- Common symptoms include numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand and fingers.
- Risk factors for developing this syndrome include repetitive hand movements and certain health conditions.
- Diagnosis involves physical examinations and may include nerve conduction studies for confirmation.
- Effective treatments range from lifestyle changes and splinting to surgical options in severe cases.
What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
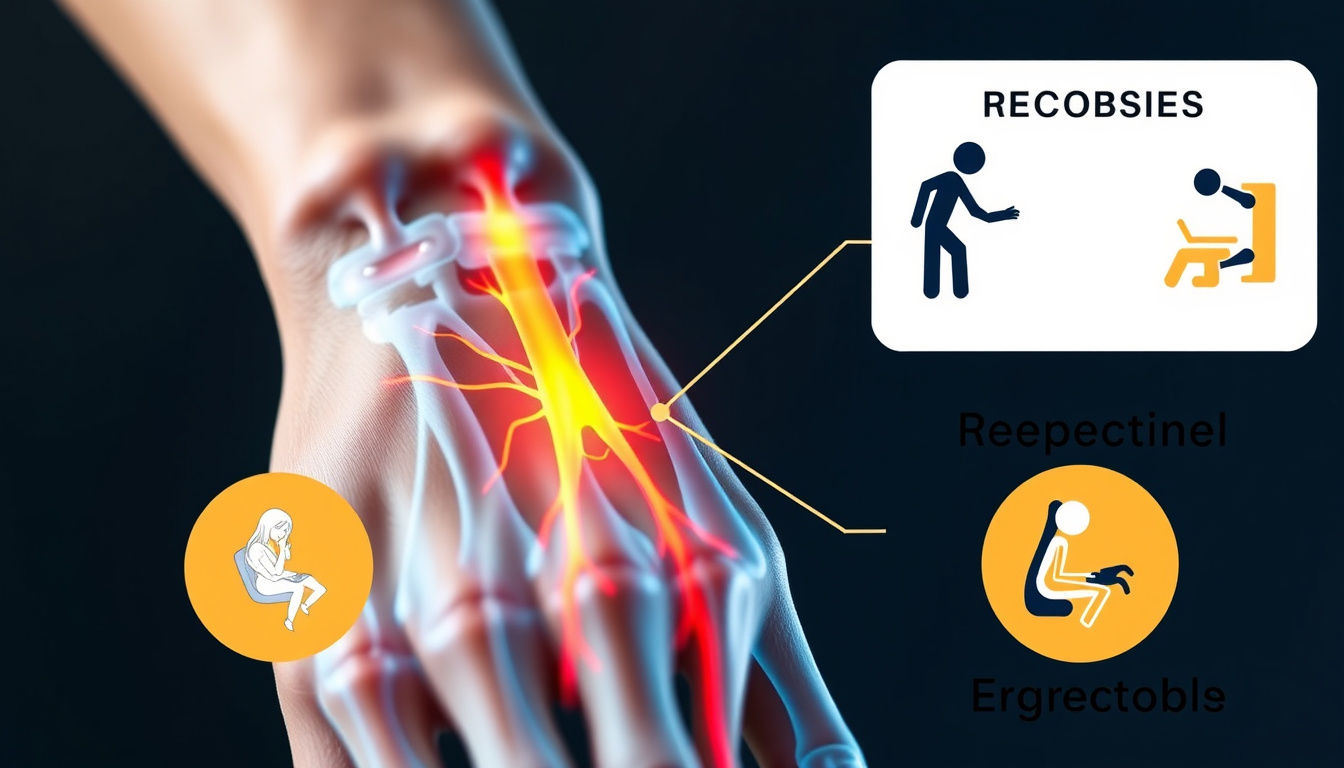
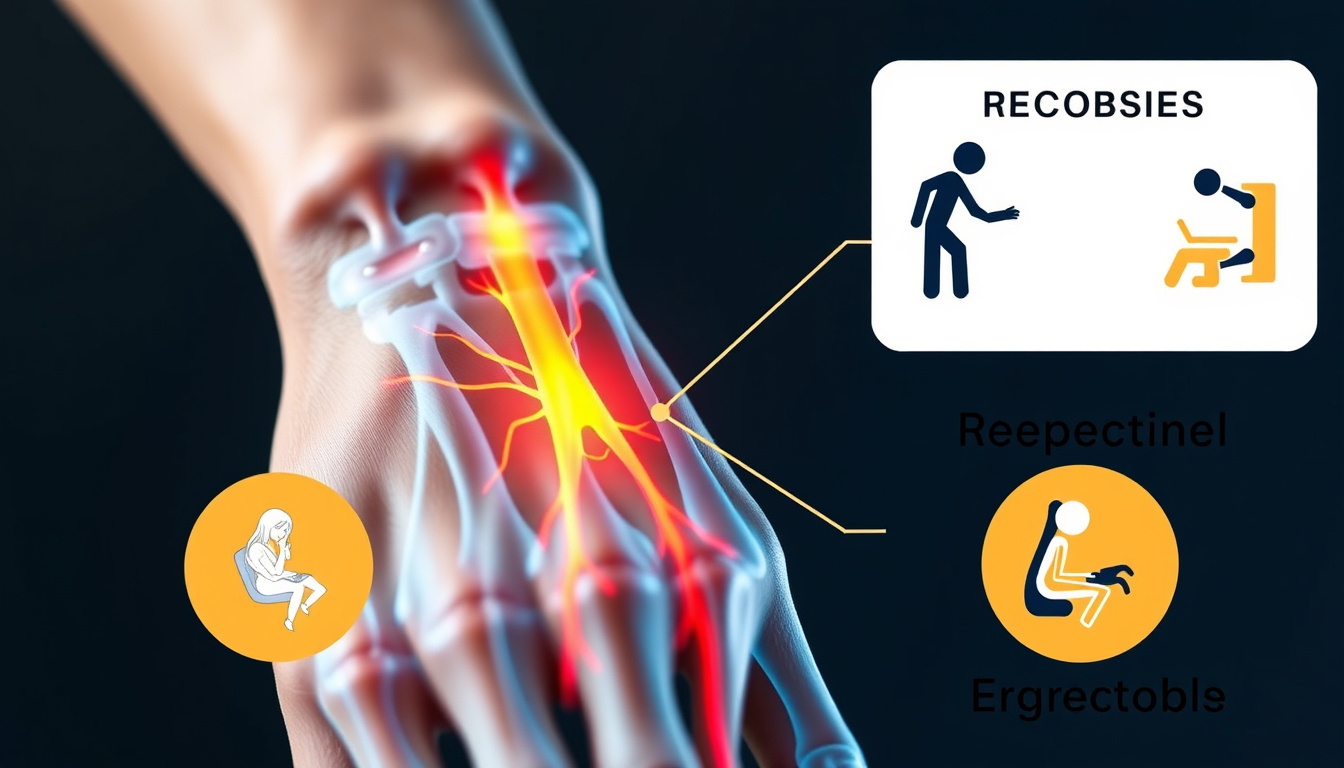
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a common condition that affects the hand and wrist, resulting from pressure on the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the palm of the hand. This syndrome is characterized by symptoms such as tingling, numbness, and pain in the fingers, particularly the thumb, index, middle, and part of the ring finger. These sensations often worsen at night or with repetitive activities, making it a prevalent condition among individuals who engage in extensive computer work or manual tasks. Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is crucial, as early diagnosis and intervention can lead to effective treatment options, helping to prevent long-term damage and improve quality of life.
Common Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
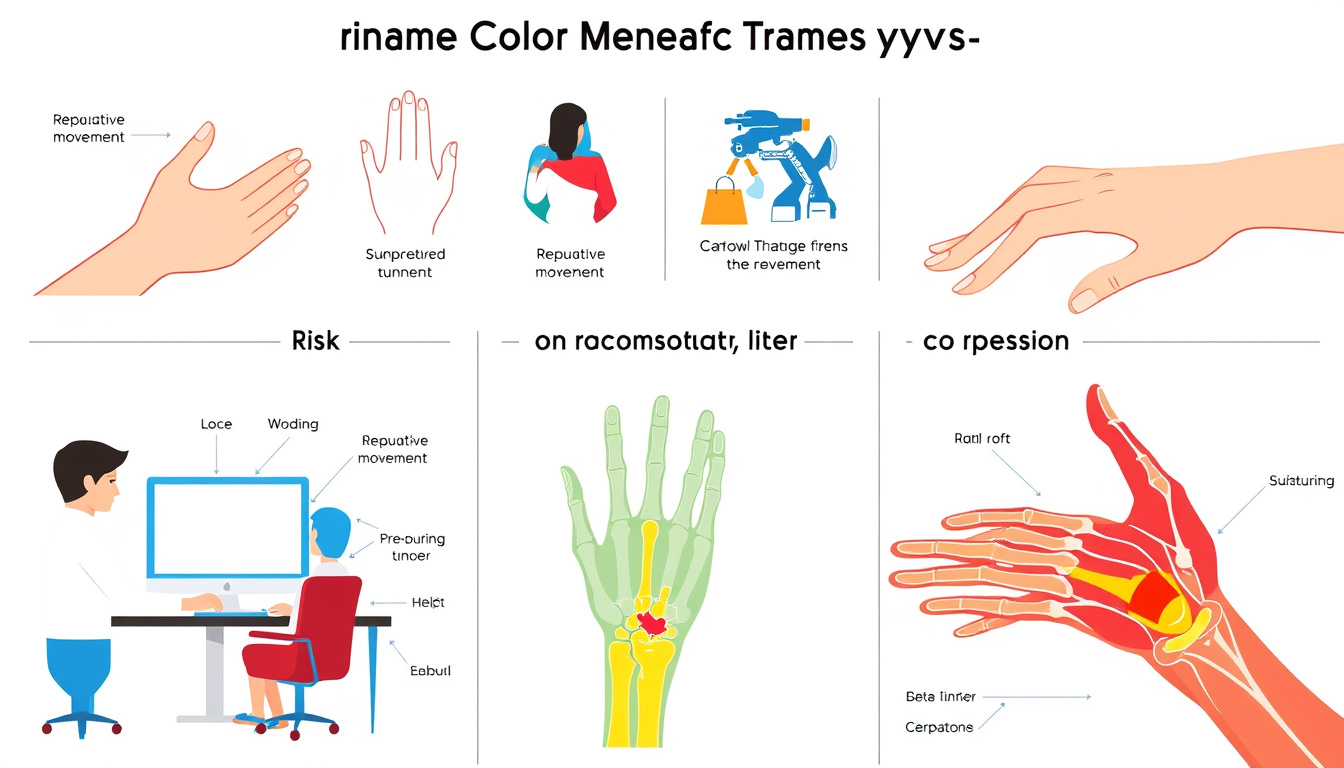
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a condition that arises when the median nerve, which runs through the carpal tunnel in your wrist, becomes compressed. This condition can lead to a variety of common symptoms that may vary in intensity. Individuals often experience numbness or tingling in the fingers, frequently affecting the thumb, index, and middle fingers. Pain can radiate from the wrist up into the forearm or down into the hand, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks. Weakness in hand muscles is another prevalent symptom, leading to struggles with gripping objects or performing fine motor tasks. Additionally, many people report symptoms that worsen at night, disrupting sleep and impacting daily productivity. Recognizing these symptoms early on is crucial for seeking appropriate treatment and preventing progression of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
‘The only way to do great work is to love what you do.’ – Steve Jobs
Causes and Risk Factors for Developing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a prevalent condition that occurs when the median nerve, which runs through the wrist, becomes compressed. Understanding the causes and risk factors for developing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is crucial for prevention and early intervention. One of the primary causes of CTS is repetitive hand movements, often seen in professions that require extensive typing or assembly work. Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and thyroid dysfunction, can heighten the risk of nerve compression. Pregnant women may also experience temporary Carpal Tunnel Syndrome due to fluid retention, which can occur during the later stages of gestation. Other risk factors include obesity, which can contribute to increased pressure in the wrist area, and a genetic predisposition, as some individuals may have a narrower carpal tunnel space inherent to their anatomy. By recognizing these causes and risk factors, individuals can better manage their activities and mitigate the chances of developing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
Diagnosis: How Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is Identified
Diagnosing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) typically begins with a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional, who will review the patient’s medical history and discuss the symptoms they are experiencing. Common signs include numbness, tingling, and pain in the fingers, especially the thumb and first three fingers, which may worsen at night. Physical examinations often include specific tests, such as the Tinel’s sign, where the doctor taps on the wrist to elicit symptoms, or the Phalen’s maneuver, where the patient holds their wrists in a flexed position to provoke discomfort. Additionally, nerve conduction studies and electromyography may be employed to assess the electrical activity and function of the median nerve. These diagnostic methods are vital for confirming Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and ruling out other similar conditions, ensuring that patients receive effective treatment to alleviate their discomfort.
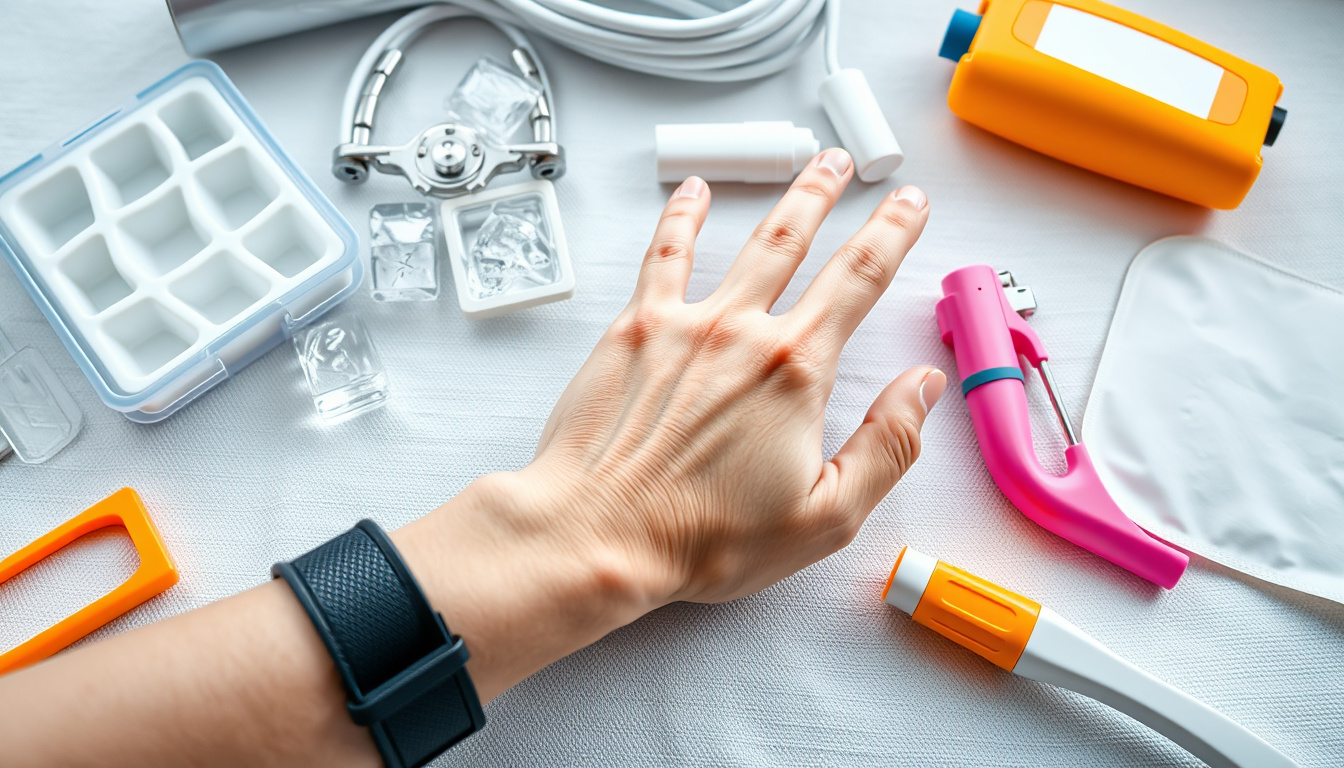

Effective Treatment Options for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a condition that results from pressure on the median nerve, which can lead to pain, numbness, and weakness in the hand and wrist. If you or someone you know is suffering from this condition, understanding the effective treatment options available is crucial for relief and recovery. Initial treatments often include wrist splints, which keep the wrist in a neutral position to reduce pressure on the nerve, especially during sleep. Alongside physical therapy, which involves specific exercises designed to strengthen the wrist and improve flexibility, anti-inflammatory medications may also be prescribed to alleviate pain and swelling. For those with more severe symptoms or who do not respond to conservative treatments, corticosteroid injections can provide both pain relief and reduce inflammation in the affected area. In persistent cases, surgical intervention to relieve the pressure on the median nerve may be necessary. Ultimately, the right approach to treating Carpal Tunnel Syndrome will depend on the severity of your symptoms and should be determined in consultation with a healthcare professional.
Preventing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Tips for Hand Health
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a common condition that affects the hands and wrists, leading to numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand. Preventing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome involves a combination of ergonomic practices, regular exercise, and awareness of body mechanics. Start by ensuring that your work environment is ergonomically friendly; adjust your desk height and keyboard position to keep your wrists in a neutral position. Incorporating wrist stretching and strengthening exercises into your daily routine can significantly help in maintaining flexibility and reducing stiffness. Additionally, take frequent breaks to relieve pressure on the wrists during prolonged typing or repetitive tasks. Being mindful of your hand positions and making conscious adjustments throughout the day can help decrease the risk of developing this debilitating condition. By following these preventive measures, you can promote overall hand health and significantly lower the likelihood of experiencing symptoms associated with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.

Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.